Rising sea levels, stronger storms, and increasing rainfall have made flood control and erosion prevention critical for coastal, riverside, and low-lying areas. Traditional methods using timber, steel, or concrete often face corrosion, high maintenance, or structural failure. PVC sheet piles provide a durable, cost-effective, and environmentally safe alternative.

PVC sheet piles are high-strength interlocking panels made of polyvinyl chloride (PVC). They form continuous walls capable of resisting water pressure, soil lateral pressure, and erosion forces.
Key Material Properties and Performance Indicators:
Density: 1.4–1.5 g/cm³
Tensile Strength: 45–55 MPa
Flexural Strength: 70–90 MPa
Temperature Resistance: -40°C to +60°C
UV Stabilization: ASTM G154 Level 3, suitable for prolonged sunlight exposure
Corrosion Resistance: Resistant to saltwater, freshwater, acidic and alkaline soils
Service Life: Over 30 years in marine environments
Weight: Approximately 40 times lighter than steel, facilitating transport and installation

PVC sheet piles can be installed in coastal and riverside areas to manage water overflow and prevent property damage.
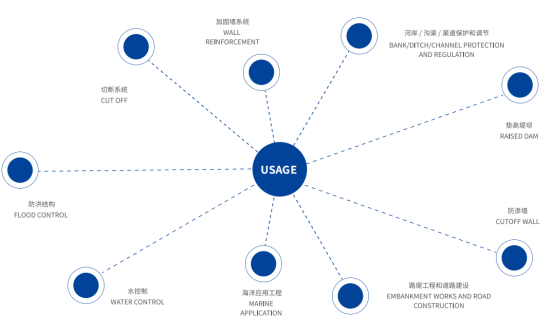
1. Seawalls and Bulkheads
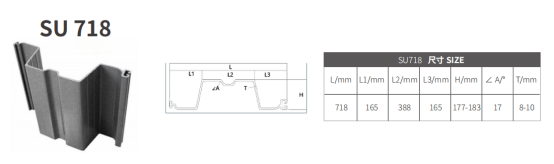
Profile: W-Type interlocking PVC sheet pile
Width: 718 mm, Depth: 180 mm, Thickness: 12–16 mm
Water Pressure Resistance: Up to 8 kPa per meter height
Installation Depth: 2–6 m depending on soil and water conditions
Creates a continuous barrier blocking tidal surges and floods with minimal seepage.
2. Cutoff Walls for Flood Zones
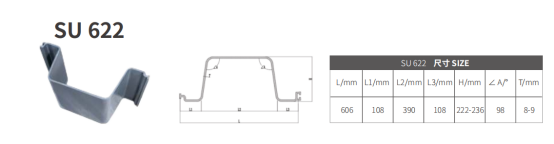
Profile: U-Type for high water retention
Depth: 1–4 m for temporary barriers, up to 6 m for permanent walls
Advantages: Rapid installation, reusable in emergency scenarios
Design Considerations:
Match pile depth to expected flood levels with a 1.2–1.5 safety factor
Consider soil type (sand, clay, silt) for driving method and stability
Integrate with drainage or pumping systems to manage overflow
PVC sheet piles protect soil from water and wind erosion, stabilizing slopes and shorelines.
1. Retaining Walls
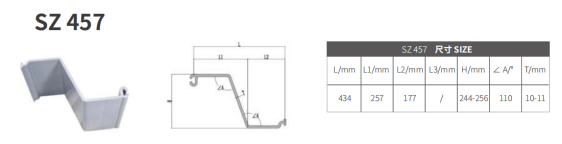
Profile: Z-Type, flexible and strong for slope retention
Height: 1–5 m
Lateral Soil Pressure Resistance: Up to 20 kPa
Backfill Material: Sand, gravel, or soil for additional stability
2. Shoreline Stabilization
Designed to absorb wave energy without deformation
UV stabilized PVC maintains structural integrity under sunlight
Low maintenance: No repainting or corrosion protection required
Integration and Combination:
Can be combined with concrete capping, sandbags, or vegetated slopes
Can integrate with riprap or geotextiles for enhanced erosion protection
1. Planning and Design
Determine wall type: seawall, retaining wall, bulkhead, or cutoff wall
Analyze soil conditions, water depth, wave or flood pressure, and environmental factors
2. Selection of Profiles
W-type: High-strength seawalls and bulkheads
Z-type: Flexible retaining walls
U-type: Cutoff walls or cofferdams for maximum water resistance
3. Installation
Use a pile driver, hydraulic hammer, or vibration hammer to drive piles
Interlock panels to form a continuous wall
Backfill with soil, sand, or gravel for additional stability
4. Maintenance
Inspect joints and panels periodically
Remove debris or sediment buildup to ensure long-term performance
Minimal maintenance compared to steel or timber, no corrosion concerns
Installation Reference Data:
Typical installation speed: 5–8 meters per hour per pile driver
Anchoring recommended for walls over 4 m high or in high-wave areas
Pre-drilling may be required in dense soil or rocky terrain
