Cooling towers are critical components in various industrial applications, from power plants and HVAC systems to chemical and petrochemical processing. Their primary function is to dissipate excess heat by transferring heat from water to the surrounding air. At the heart of this process lies the cooling tower fill, a specially designed material that enhances the efficiency of heat exchange. By increasing the surface area available for water and air interaction, the cooling tower fill ensures optimal performance and energy efficiency.

The core principle of any cooling tower is the exchange of heat between warm water and cooler air. Cooling tower fill is essential because it facilitates better heat dissipation by creating more surface area for water and air to interact. This is achieved in two primary ways:
Splash Fill: This design involves large, splashy surfaces that cause the water to break up into smaller droplets, increasing its surface area. The splashing action creates turbulence, improving heat exchange. This type of fill is typically used in cooling towers with high water flow rates, where the need for a high rate of heat transfer is crucial.
Film Fill: A film fill consists of thin sheets of material that the water flows over, forming a thin film. This design allows for maximum surface area and better heat exchange efficiency compared to splash fills. Film fills are typically used in towers with lower flow rates and are ideal for applications requiring energy efficiency and better overall heat transfer.
Both fill designs are critical to ensuring the cooling tower operates efficiently. The choice of fill depends on factors such as water flow rate, ambient temperature, and the specific cooling needs of the application.
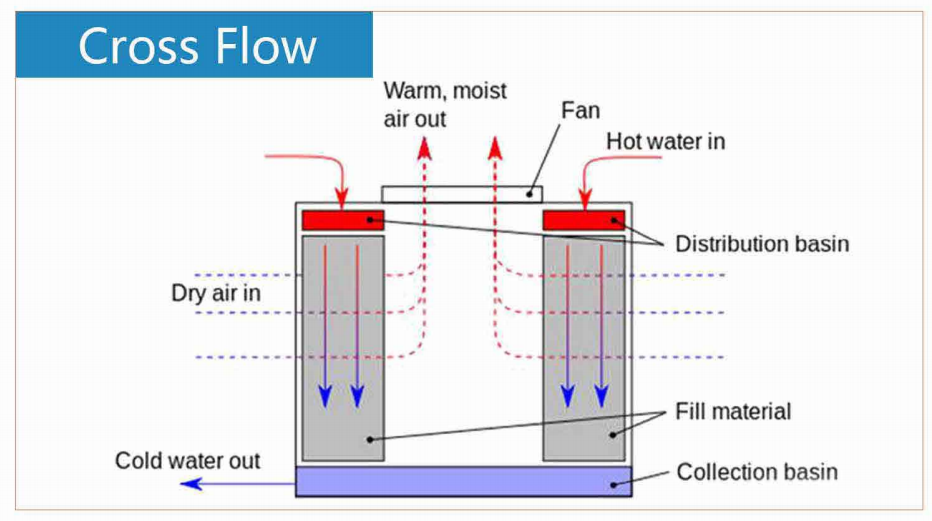
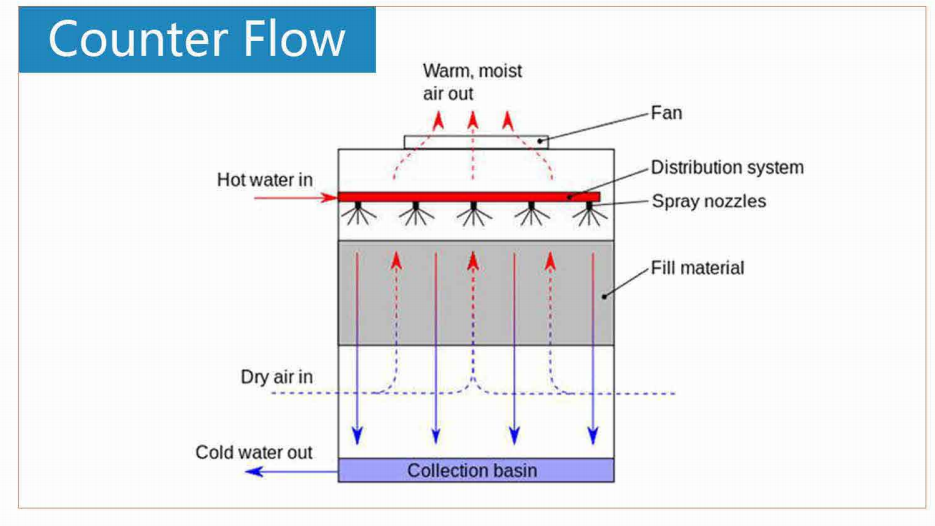
To maximize the effectiveness of cooling tower fills, it is essential to understand the key design considerations that influence performance:
Material Selection: Cooling tower fills are typically made from materials that are resistant to corrosion and degradation due to exposure to water and air. Common materials include:
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride): PVC is widely used because it is cost-effective, durable, and resistant to chemicals and UV degradation.
PP (Polypropylene): This material is known for its high temperature resistance, making it suitable for high-heat applications.
PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate): PET offers excellent strength and durability, making it ideal for cooling towers in harsh environments.
The selection of the right material is vital not only for the longevity of the fill but also for maintaining cooling tower efficiency.
Fill Configuration: The configuration of the cooling tower fill impacts airflow and water distribution. A well-designed fill ensures that the water is evenly distributed, preventing areas where water may stagnate and reduce efficiency. The arrangement of fill packs, whether in a vertical or horizontal alignment, can further influence the airflow and the heat transfer rate.
Air and Water Flow Distribution: Uniform distribution of water and air is critical for effective cooling. A good fill design helps ensure that the water evenly flows over the fill media, maximizing the contact time with the air. Poor distribution can lead to localized overheating, reducing the overall cooling efficiency.
Maintenance Considerations: The design of the cooling tower fill should also take into account the ease of cleaning and maintenance. Cooling towers are subject to scaling, biofilm formation, and corrosion, which can reduce their efficiency over time. Therefore, selecting materials that are easy to clean and resistant to these issues is vital.

Cooling tower fills are integral to a wide range of industrial applications. Their role extends beyond just heat dissipation; they contribute to energy savings, water conservation, and operational efficiency. Let's explore some of the key industries where cooling tower fills play a critical role:
Power Generation: In power plants, cooling towers are used to manage the heat generated during the electricity production process. The fill’s design in these applications is crucial to ensuring maximum heat dissipation, as power plants often deal with extremely high water temperatures. Both splash and film fills may be used depending on the specific cooling tower requirements.
HVAC Systems: Large commercial and industrial HVAC systems use cooling towers to regulate the temperature of the water circulating in the system. Here, cooling tower fills help maintain optimal operating conditions by efficiently cooling the water used for heat exchange in air conditioning and refrigeration processes.
Chemical and Petrochemical Processing: Cooling towers in these industries must handle not only high temperatures but also the presence of chemicals in the water. Cooling tower fills designed with corrosion-resistant materials such as PP and PET ensure durability while maintaining efficient cooling in the face of these harsh conditions.
Oil Refineries: Oil refineries require highly efficient cooling systems to deal with the intense heat generated during the refining process. The design and material selection of cooling tower fills are critical for preventing damage from oil residues and ensuring the cooling process operates smoothly.
Food and Beverage: The food and beverage industry uses cooling towers to manage the heat generated during production and processing. The fills in these applications must be designed for easy cleaning and maintenance to prevent contamination.
Mining and Metals: Cooling towers in mining operations are tasked with cooling water used in smelting and ore processing. These applications require robust cooling systems that can handle the high temperatures and the presence of metals and other contaminants in the water.
Environmental Impact and Energy Efficiency: One of the primary benefits of cooling tower fills is their ability to improve energy efficiency. By enhancing the heat transfer process, cooling towers require less energy to achieve the same cooling effect, thereby reducing operational costs. Additionally, modern cooling tower designs aim to minimize water consumption by reducing evaporation losses.
When selecting a cooling tower fill, several factors need to be considered to ensure it meets the specific needs of the application:
Water Temperature and Flow Rate: High-temperature applications typically benefit from splash fills, while low-flow systems may perform better with film fills.
Environmental Conditions: If the cooling tower operates in a corrosive environment, materials like PP or PET are better suited due to their superior resistance to chemical degradation.
Space and Configuration: The available space and the required tower configuration will dictate the fill design, with vertical or horizontal alignments being chosen based on air and water flow requirements.
Maintenance and Durability: Regular maintenance is essential for optimal performance. Selecting a fill material that is easy to maintain and clean will reduce downtime and ensure long-term efficiency.
Cooling tower fills are an indispensable part of modern industrial cooling systems. By increasing the surface area for heat exchange, they enhance the efficiency of cooling towers, helping industries meet their energy, water, and environmental goals. Whether it’s power generation, HVAC systems, or chemical processing, the right cooling tower fill ensures reliable performance and sustainable operation. As industries continue to focus on energy efficiency and environmental impact, the design and application of cooling tower fills will evolve to meet these new challenges.
By understanding the principles, design considerations, and applications of cooling tower fills, companies can optimize their cooling processes, reduce costs, and contribute to a more sustainable future.