Address
No.88, Qilian Street, High-Tech Zone, Shijiazhuang, Hebei 050000, China
Tel
+86 311 6779 0805
+86 188 4915 5666


### **Raschig Rings: Product Overview**
**Raschig Rings** are one of the earliest and most widely used types of random packing in industrial processes such as distillation, absorption, and gas scrubbing. Invented by German chemist Friedrich Raschig in the early 20th century, these simple cylindrical packings remain relevant due to their durability, low cost, and versatility in basic separation tasks.
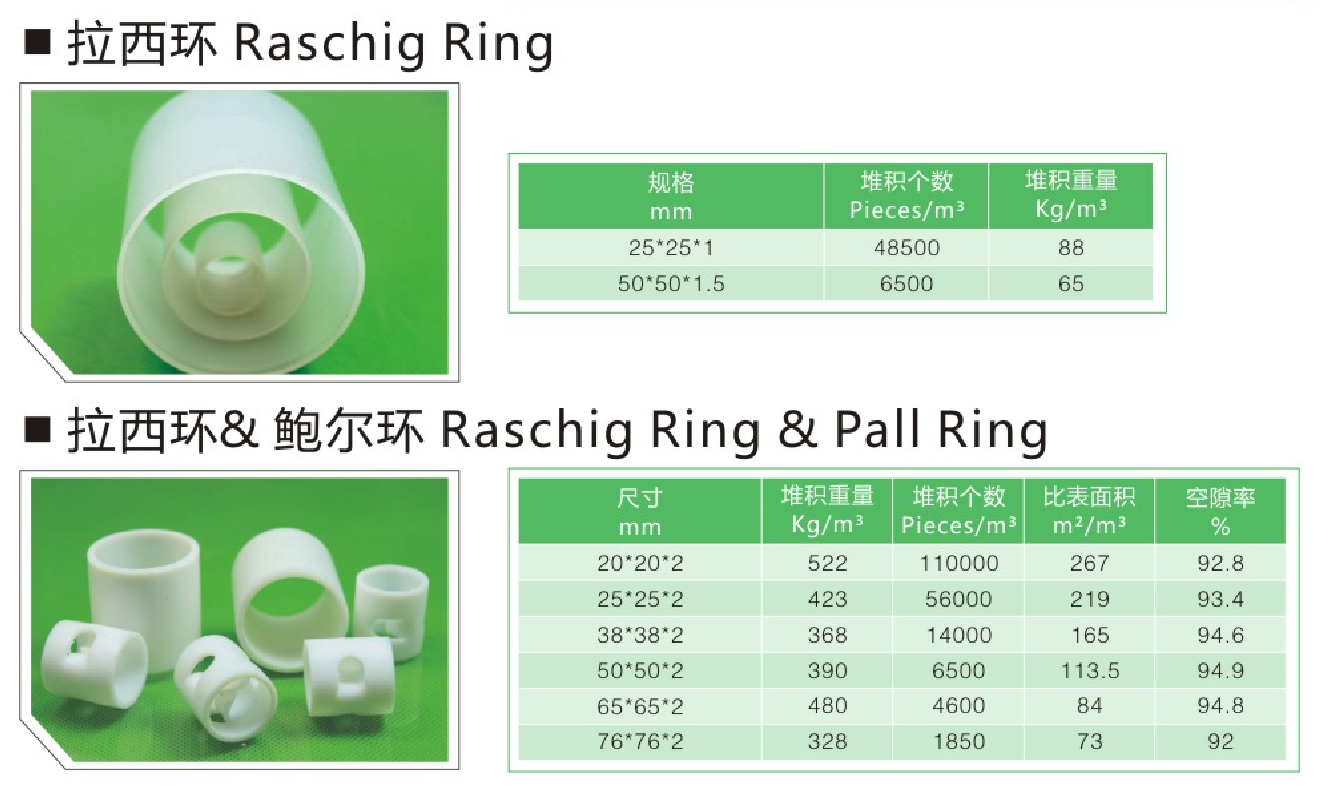
### **Structural Features**
1. **Simple Cylindrical Geometry**:
- Hollow cylinders with a length equal to their diameter, made from inert materials.
- Smooth internal and external surfaces with no internal baffles or perforations.
2. **Material Diversity**:
- **Ceramic**: Traditional choice for high-temperature and corrosive environments.
- **Metal**: Stainless steel, carbon steel, or aluminum for high-strength applications.
- **Plastic**: Polypropylene (PP) or PVC for lightweight, acid/alkali-resistant systems.
3. **Basic Design**:
- Lacks advanced features like internal tabs or ribs, relying on surface area for gas-liquid contact.
### **Classification**
1. **By Material**:
- **Ceramic Raschig Rings**: Used in sulfuric acid plants, high-temperature gas drying.
- **Metal Raschig Rings**: Ideal for high-pressure distillation or reactive chemical processes.
- **Plastic Raschig Rings**: Common in wastewater aeration or mild chemical scrubbing.
2. **By Size**:
- Standard diameters range from **6 mm to 150 mm**; smaller sizes for precision, larger for high-capacity systems.
### **Key Advantages**
1. **Cost-Effective**:
- Simple manufacturing process makes them cheaper than advanced packings like Pall Rings or structured packing.
2. **Chemical Inertness**:
- Ceramic and plastic variants resist corrosion from acids, alkalis, and organic solvents.
3. **High Temperature Tolerance**:
- Ceramic rings withstand temperatures up to **1000°C**, ideal for thermal processes.
4. **Mechanical Strength**:
- Metal and ceramic rings are robust under high pressure or mechanical stress.
### **Applications**
1. **Distillation Columns**:
- Basic separation of liquid mixtures (e.g., alcohol-water systems).
2. **Absorption Towers**:
- Gas scrubbing (e.g., HCl or SO₂ removal in chemical plants).
3. **Drying Systems**:
- Moisture removal from gases using desiccants like silica gel.
4. **Wastewater Treatment**:
- Biofilm carriers in trickling filters or aeration basins.
5. **Catalyst Support**:
- Ceramic rings act as catalyst substrates in reactors.
### **Comparison with Advanced Packings**
- **Vs. Pall Rings**:
- Raschig Rings have **30–50% lower mass transfer efficiency** and **higher pressure drop** due to their non-turbulent flow design.
- **Vs. Multi-Sphere Hollow Balls**:
- Less surface area and weaker liquid redistribution capability but superior mechanical strength in ceramic/metal forms.
### **Why Choose Raschig Rings?**
They are ideal for **low-budget projects**, **high-temperature/corrosive environments**, or processes where simplicity and reliability outweigh the need for ultra-high efficiency.